|
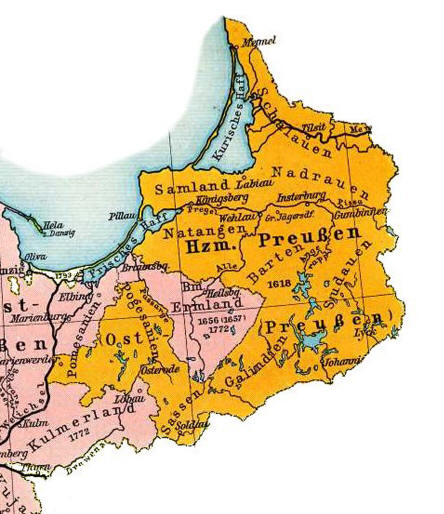
Samland
Sambia was originally sparsely populated by the Sambians. The
region was conquered by the German Teutonic Knights during the
13th century and the Bishopric of Samland became, along with
Bishopric of Pomesania, Bishopric of Ermland, and Bishopric of
Culm, one of the four dioceses of Prussia in 1243. Settlers from
the HolyRoman Empire began colonizing the region, while the Sambian Prussians were gradually assimilated. The peninsula was
the last area in which the Old Prussian language was spoken before
becoming extinct at the beginning of the 18th century.
The peninsula became part of the Duchy of Prussia when the
Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights was secularized in 1525.
This duchy was inherited by the Margraviate of Brandenburg in
1618, and the Hohenzollern monarchs eventually proclaimed the
Kingdom of Prussia in 1701. Sambia became part of the Province of
East Prussia in 1773. Prussia completed the unification of Germany
with the creation of the German Empire in 1871.
After World War I, Sambia and East Prussia became exclaves of
Weimar Germany. In 1945 after World War II, East Prussia was
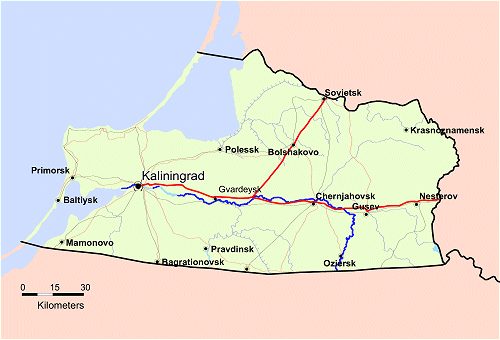
partitioned between Poland and the Soviet Union. Sambia became
part of the Kaliningrad Oblast, named after the nearby city of
Kaliningrad (historic German:
Königsberg or historic in Slavic languages Kráľovec),
and its German inhabitants were expelled.
Sambia was subsequently repopulated with Russians and
Belarusians. It has two famous seaside resorts, Zelenogradsk (Cranz)
and Svetlogorsk (Rauschen).
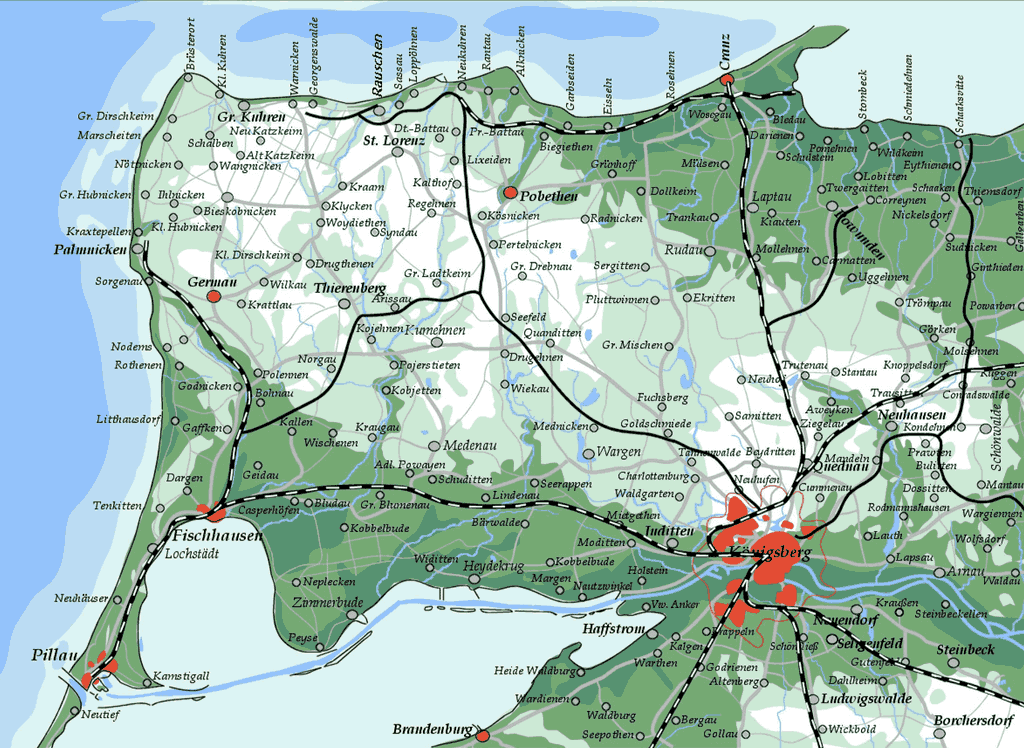
Geography and geology
Baedeker describes Samland as "a fertile and partly-wooded
district, with several lakes, lying to the north of Königsberg"
(now Kaliningrad). The highest point, 360 feet, is found twelve
miles north of Pereslavskoe (Drugehnen) at the ski resort
then called the Galtgarben.. There also used to be a Samland
railway station. Today, the Pereslavskoe railway station serves
the "Blue Arrow" railway line from Kaliningrad to Svetlogorsk.
Amber
Amber has been found in the area for over a thousand years,
especially on the coast near Kaliningrad. In 1900, amber was
chiefly exported to the East for crafting into pipe mouthpieces
and ornaments. Until 1918, the right to collect amber was
restricted to the Hohenzollern dynasty of Prussia; visitors to
Samland's beaches were forbidden to pick up any fragments they
found. It is said that an ancient trade route known as the Amber
Road led from the Old Prussian settlements of Kaup (in Sambia) and
Truso (near Elbląg) to the Black Sea and further east.
Used within the scope of GNU Free Documentation License,
Wikipedia®
|